Overfitting and Underfitting
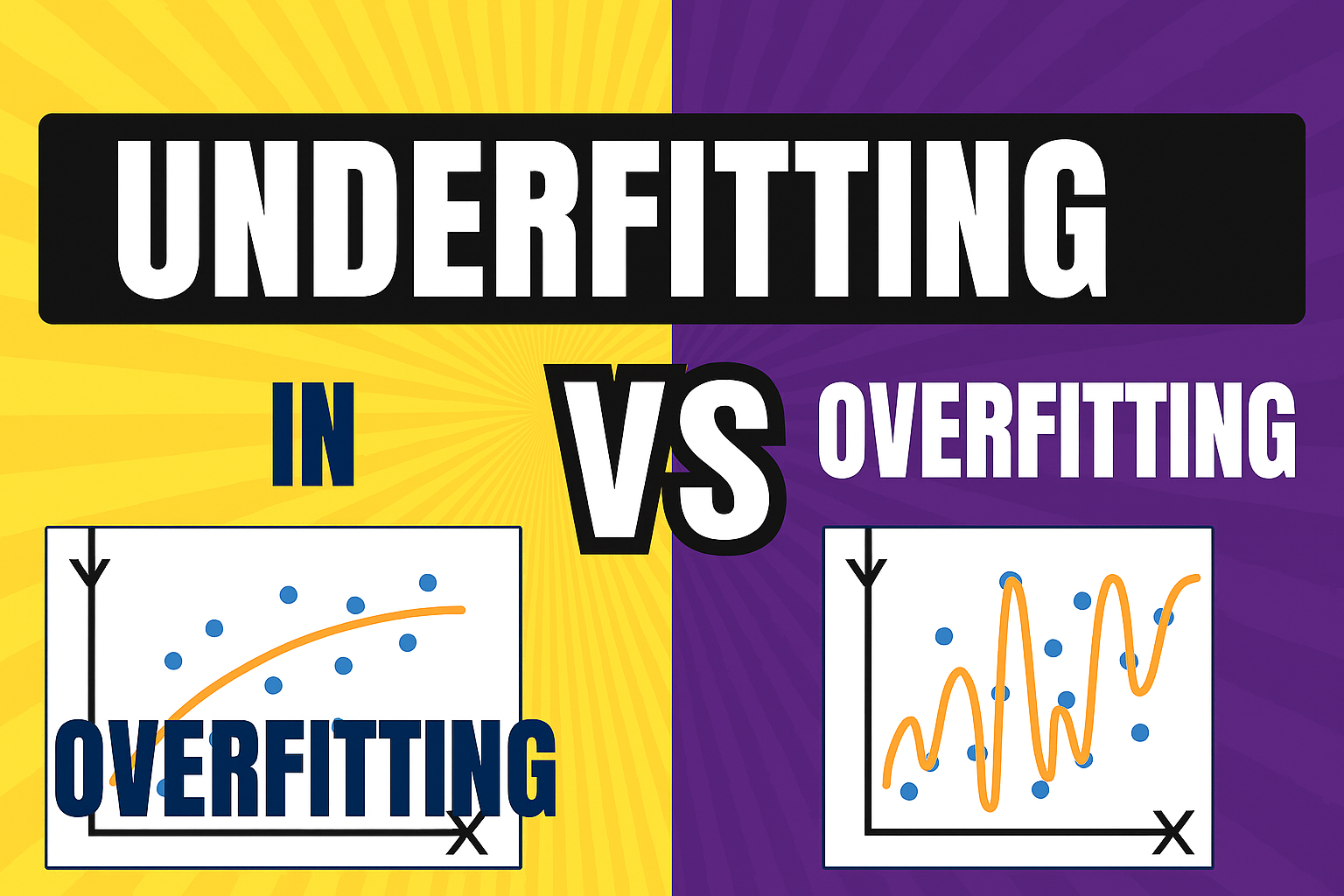
🎭 1. OVERFITTING = Too much focus on the past
Layman example:
Imagine you're preparing for an exam by memorizing every question from past papers word-for-word.
But in the real exam, even one small change in the question confuses you.
In ML terms:
-
Model learns too much detail, even noise.
-
Performs great on training data but poor on real/new data.
-
Like a student who memorizes instead of understanding.
Signs of Overfitting:
✔ High accuracy on training
✘ Low accuracy on testing
✔ Model is too complex
🪫 2. UNDERFITTING = Too simple to learn anything
Layman example:
You study only headlines of the chapter, not details.
In exam, you can't answer anything properly because you never learned enough.
In ML terms:
-
Model is too simple.
-
Cannot capture patterns.
-
Low accuracy on both training and testing.
Signs of Underfitting:
✘ Low training accuracy
✘ Low testing accuracy
✔ Model is too simple
🔧 3. REGULARIZATION = The tool to fix overfitting
Layman example:
Think of regularization like telling the student:
"Stop memorizing every word. Focus on the important concepts only."
Regularization controls how complicated a model can become.
It forces the model to generalize instead of memorizing.
Simple analogy:
-
Overfitting = a child drawing with too many tiny details
-
Regularization = parent telling: "Use fewer lines → Keep it simple."
What regularization does:
✔ Penalizes overly complex models
✔ Reduces noise learning
✔ Improves performance on new (test) data
🚀 One-line memory trick
Overfitting = Overthinking
Underfitting = Under-thinking
Regularization = Keeping thinking in control
✅ MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) (Layman-friendly, exam-friendly)
1. Overfitting happens when a model:
A. Learns too little
B. Learns noise and unnecessary details
C. Ignores the data
D. Has no data
Answer: B
2. Underfitting happens when a model:
A. Learns too much
B. Learns too little
C. Has perfect accuracy
D. Has no testing data
Answer: B
3. Overfitting leads to:
A. High training accuracy, low testing accuracy
B. Low training accuracy, high testing accuracy
C. Same accuracy on both
D. No accuracy
Answer: A
4. Underfitting leads to:
A. High accuracy on training
B. Low accuracy on both training and testing
C. High accuracy on testing only
D. No training required
Answer: B
5. What is the purpose of regularization?
A. Increase model size
B. Add noise
C. Reduce overfitting
D. Make model slow
Answer: C
6. Overfitting is similar to a student who:
A. Studies nothing
B. Memorizes entire book word-for-word
C. Understands concepts
D. Writes randomly
Answer: B
7. Underfitting is similar to a student who:
A. Memorizes everything
B. Reads only chapter names
C. Writes long answers
D. Uses formulas
Answer: B
8. Regularization encourages model to be:
A. More complex
B. Extremely large
C. Simpler
D. Slow
Answer: C
9. Which is a sign of overfitting?
A. Model does well on new data
B. Model performs badly on training data
C. Model performs very well on training but badly on test
D. Model predicts all zeros
Answer: C
10. Which is NOT a cause of underfitting?
A. Too simple model
B. Too few parameters
C. Too complex model
D. Too little training
Answer: C
11. Which technique reduces overfitting?
A. Increasing model size
B. Adding regularization
C. Removing regularization
D. Increasing noise
Answer: B
12. A model with high bias will most likely:
A. Underfit
B. Overfit
C. Do both
D. Do neither
Answer: A
13. A model with high variance will most likely:
A. Underfit
B. Overfit
C. Ignore data
D. Improve slowly
Answer: B
14. L2 regularization is also known as:
A. Dropout
B. Ridge
C. Lasso
D. Boosting
Answer: B
15. L1 regularization is also known as:
A. Ridge
B. Bagging
C. Lasso
D. Random Forest
Answer: C
16. Dropout is mainly used in:
A. Linear Regression
B. SVM
C. Neural Networks
D. Decision Trees
Answer: C
17. If a model performs bad on both training & testing, it is:
A. Overfitting
B. Good fit
C. Underfitting
D. Perfect
Answer: C
18. If a model performs very well on training data only, it is:
A. Generalizing
B. Underfitting
C. Overfitting
D. Normal
Answer: C
19. Regularization helps a model:
A. Memorize more
B. Learn less important patterns
C. Generalize better
D. Remove labels
Answer: C
20. The goal of a good ML model is to:
A. Perfectly learn training data
B. Fail on real data
C. Generalize to unseen data
D. Be as complex as possible
Answer: C
