Mastering Logistic Regression
Logistic Regression Overview
Logistic regression is a fundamental statistical and machine learning method used for predicting binary outcomes, such as yes/no, true/false, or success/failure. Instead of modeling the target directly, it models the probability that an observation belongs to a particular class using the logistic (sigmoid) function. This makes it especially useful when you need interpretable coefficients that show how each feature influences the odds of an outcome, while still providing robust predictive performance on many real‑world classification problems.
In practice, logistic regression is widely applied in areas like credit scoring, medical diagnosis, marketing response prediction, and risk assessment. It supports regularization techniques to prevent overfitting and can be extended to multiclass problems using strategies such as one‑vs‑rest. Because it outputs probabilities, it integrates naturally with decision thresholds and evaluation metrics like ROC curves, precision, recall, and F1‑score, making it a versatile and reliable baseline model for many classification tasks.
What is Logistic Regression?
Logistic Regression is a classification algorithm used to predict binary outcomes—situations where the answer is yes or no, pass or fail, spam or not spam, disease or no disease.
Despite the word regression in its name, logistic regression is not used for predicting continuous values. Instead, it predicts probabilities.
Real-Life Examples
-
Will a student pass or fail based on marks?
-
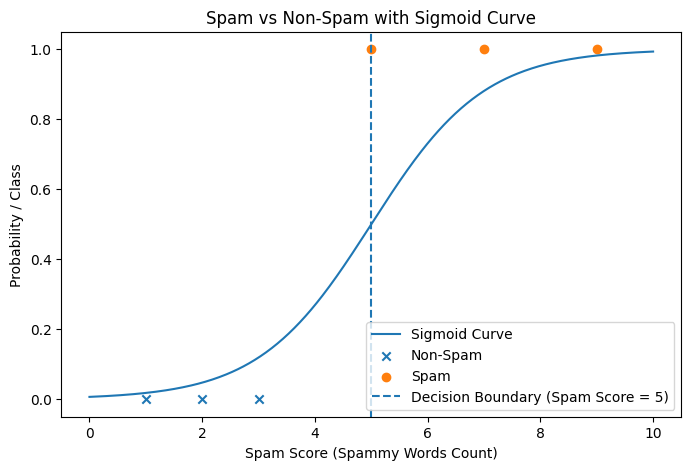
Is an email spam or non-spam?
-
Will a customer buy or not buy a product?
-
Is a transaction fraudulent or genuine?
In all these cases, the outcome has two possible classes.
Why Not Linear Regression?
Linear regression outputs values like:
-
120
-
−15
-
2.7
But probabilities must lie between 0 and 1.
❌ Linear regression can produce values outside this range, making it unsuitable for classification.
Logistic regression solves this by converting outputs into probabilities.
Logistic Regression uses a sigmoid function to convert linear values into probabilities between 0 and 1.
Mathematical Foundation
Step 1: Linear Combination
Just like linear regression:
z=b0+b1x1+b2x2+⋯+bnxn
Where:
-
x1,x2,x3...…..are input features
-
b0,b1,b2,b3............are weights
Step 2: Sigmoid Function
The sigmoid function converts z into probability:
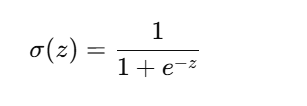
Properties of Sigmoid:
-
Output range: 0 to 1
-
Smooth, S-shaped curve
-
Ideal for probability estimation
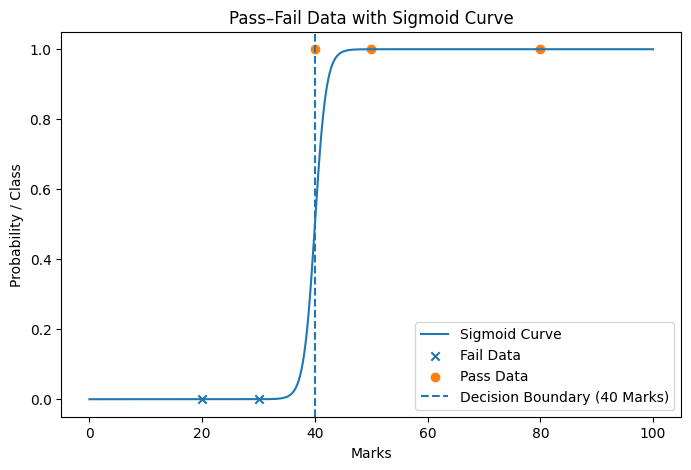
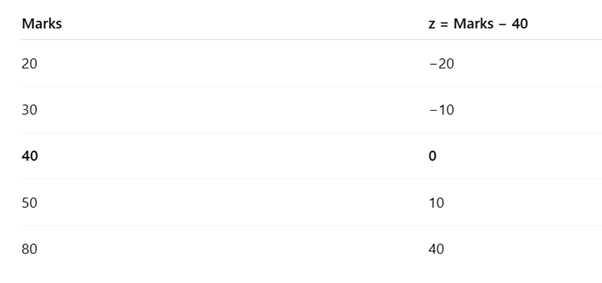
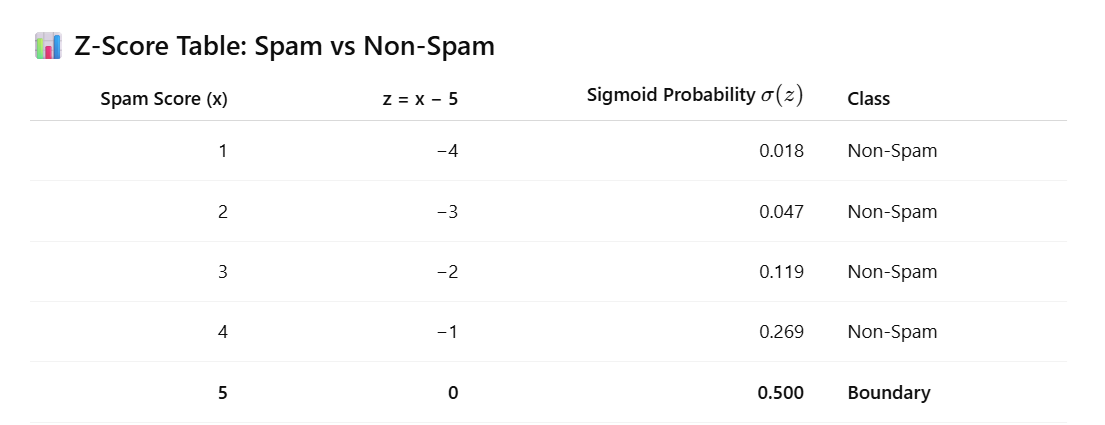
In a sigmoid function, 50% probability ALWAYS occurs at z=0
This is fixed by mathematics, not by data.
So:
-
z = 0 ⇒ probability = 50%
-
z > 0 ⇒ probability > 50%
-
z < 0 ⇒ probability < 50%
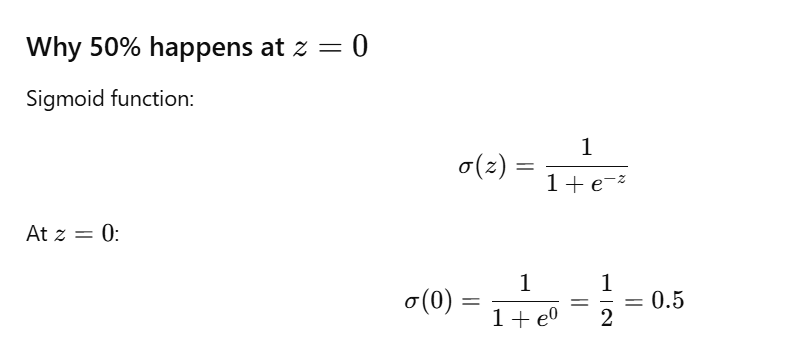

How loss works with examples (very important)
Case 1: Correct and confident prediction
- Actual result: Pass (y = 1)
- Model predicts: p = 0.95
Loss ≈ very small
👉 Model is rewarded.
Case 2: Correct but unsure 🤔
- Actual result: Pass (y = 1)
- Model predicts: p = 0.55
Loss = medium
👉 Model is correct, but not confident.
Case 3: Confident but wrong ❌ (big punishment)
- Actual result: Pass (y = 1)
- Model predicts: p = 0.05
Loss = very large
👉 Model is heavily punished.
This is the key idea behind log loss.
MCQs on Logistic Regression
1. Logistic regression is mainly used for:
A.
Predicting continuous values
B. Clustering data
C. Binary classification
D. Dimensionality reduction
✅ Answer: C
Explanation: Logistic regression is used when the output has two classes
(Yes/No, 0/1).
2. What is the output of logistic regression before applying a threshold?
A. Class
label
B. Integer value
C. Probability
D. Category name
✅ Answer: C
Explanation: Logistic regression outputs a probability between 0 and 1.
3. Which function converts the linear output into probability?
A. ReLU
B. Softmax
C. Sigmoid
D. Step function
✅ Answer: C
Explanation: The sigmoid function maps any real value into the range (0,
1).
4. The sigmoid function outputs values between:
A. −1 and 1
B. 0 and ∞
C. −∞ and ∞
D. 0 and 1
✅ Answer: D
5. If the sigmoid output is 0.5, what does it indicate?
A. Certain
failure
B. Certain success
C. Complete uncertainty
D. Invalid prediction
✅ Answer: C
Explanation: 0.5 means the model is unsure between both classes.
6. What is the most commonly used threshold in logistic regression?
A. 0.3
B. 0.4
C. 0.5
D. 1
✅ Answer: C
7. Which loss function is used in logistic regression?
A. Mean
Squared Error
B. Hinge Loss
C. Log Loss (Binary Cross-Entropy)
D. Absolute Error
✅ Answer: C
8. Why is Mean Squared Error not preferred for logistic regression?
A. It is
computationally slow
B. It does not work with probabilities
C. It gives biased results for classification
D. All of the above
✅ Answer: D
9. What happens to loss when the model is confidently wrong?
A. Loss
becomes zero
B. Loss decreases
C. Loss increases slightly
D. Loss increases sharply
✅ Answer: D
10. Logistic regression is called "regression" because:
A. It
predicts continuous values
B. It uses regression coefficients
C. It uses a linear equation internally
D. It minimizes squared error
✅ Answer: C
11. Which of the following is a valid application of logistic regression?
A. House
price prediction
B. Weather temperature prediction
C. Spam email detection
D. Stock price forecasting
✅ Answer: C
12. If z is a very large positive number, sigmoid(z) will be:
A. Close to
0
B. Close to 0.5
C. Close to 1
D. Undefined
✅ Answer: C
13. If z is a very large negative number, sigmoid(z) will be:
A. Close to
1
B. Close to 0
C. Exactly −1
D. Exactly 0.5
✅ Answer: B
14. Logistic regression assumes:
A.
Non-linear relationship between features and output
B. Linear relationship between features and log-odds
C. Features must be normally distributed
D. No need for labeled data
✅ Answer: B
15. Logistic regression belongs to which type of learning?
A.
Unsupervised learning
B. Reinforcement learning
C. Supervised learning
D. Semi-supervised learning
✅ Answer: C
