Defining Data Needs for AI(II)
Identifying Data Needs for AI Projects (Phase II)
In Phase II, we translate business objectives into concrete data requirements that can reliably power your AI solutions. We work with stakeholders to clarify use cases, define success metrics, and map the data sources needed to support them. This includes assessing current data assets, identifying critical gaps, and prioritizing what must be collected, cleaned, or integrated. The outcome is a clear, actionable data blueprint that aligns technical needs with strategic goals and reduces risk in later development stages.
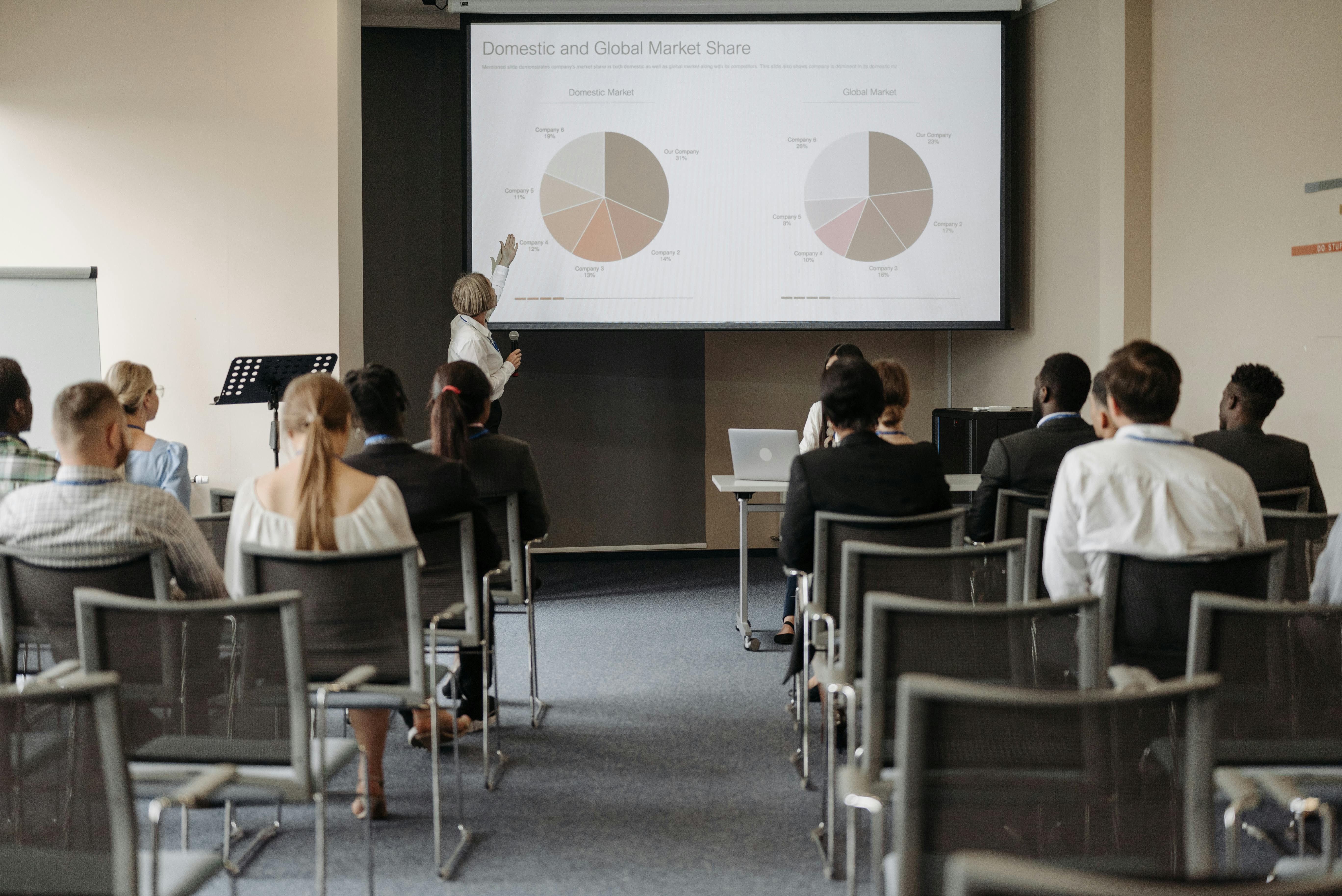

Our approach covers both quantitative and qualitative dimensions of your data landscape. We evaluate data volume, quality, accessibility, and governance, while also considering privacy, compliance, and ethical constraints. Together, we define data schemas, labeling strategies, and minimal viable datasets for experimentation. By the end of Phase II, your organization has a prioritized roadmap of data initiatives, clear ownership, and realistic timelines, ensuring that subsequent AI modeling efforts are efficient, scalable, and aligned with business value.
Artificial Intelligence projects do not fail because of weak algorithms—they fail because of poor data foundations.
Phase II of the PMI-CPMAI® framework focuses on identifying, assessing, and validating data before any model is built.
This phase answers one critical question:
Do we have the right data—ethically, legally, and practically—to support the AI solution?
Why Data Understanding Comes Before Model Building
Many organizations rush into selecting algorithms and tools. CPMAI emphasizes a disciplined, business-first approach where data readiness determines AI feasibility.
Poor data quality and governance are the leading causes of AI failure.
If data is unreliable, AI decisions will also be unreliable.
1. Translating Business Goals into Data Requirements
Every AI initiative starts with a business problem, but Phase II converts it into clear data needs.
Example
Business Goal: Reduce customer churn
Derived Data Needs:
-
Historical customer behavior
-
Transaction frequency and value
-
Support tickets and complaints
-
Definition of "churn" and time horizon
Key Outputs
-
Target variable (what AI predicts)
-
Input features (what influences outcomes)
-
Historical data window
-
Prediction timeframe
2. Identifying the Right Data Types
Different AI use cases require different kinds of data.
Common Data Categories
-
Structured data: Databases, spreadsheets, metrics
-
Unstructured data: Emails, documents, images, audio
-
Semi-structured data: Logs, JSON, XML
-
External data: Market data, weather, social signals
CPMAI stresses selecting data based on business relevance—not availability.
3. Assessing Data Availability and Accessibility
Not all required data is immediately usable.
Key Questions
-
Does the data exist?
-
Who owns the data?
-
Is it siloed across departments?
-
Can it be legally accessed and shared?
Early identification of access constraints prevents costly rework later.
4. Evaluating Data Quality and Bias
Data quality is the single most critical success factor in AI projects.
Core Data Quality Dimensions
-
Accuracy: Correct and error-free
-
Completeness: Minimal missing values
-
Consistency: Uniform meaning across systems
-
Timeliness: Up-to-date and relevant
-
Bias & representativeness: Fair reflection of reality
⚠️ Biased data leads to biased AI outcomes—an important CPMAI exam theme.
5. Privacy, Security, and Compliance Considerations
AI data must comply with legal and ethical standards.
Phase II Compliance Checks
-
Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
-
Consent and purpose limitation
-
Data anonymization or masking
-
Industry and regional regulations
If data cannot be used legally or ethically, the AI solution must be redesigned or stopped.
6. Identifying Data Gaps and Remediation Options
After assessment, teams decide whether data is:
-
✅ Sufficient to proceed
-
⚠️ Requires enrichment or labeling
-
❌ Inadequate for AI use
Remediation Strategies
-
Data cleaning and normalization
-
Feature engineering
-
External data acquisition
-
Manual or automated labeling
7. Phase II Deliverables
By the end of Phase II, organizations should have:
✔ Data requirements document
✔ Data inventory and source mapping
✔ Data quality and bias assessment
✔ Privacy and compliance review
✔ Go / No-Go recommendation
In CPMAI Phase II, understanding the properties of Big Data is essential to determine whether data is suitable, sufficient, and feasible for an AI initiative. These properties help decision-makers evaluate data readiness before any preparation or modeling begins.
-
Volume determines whether the quantity of available data is adequate to support statistically meaningful AI outcomes.
-
Velocity assesses how quickly data is generated and whether real-time or near-real-time processing is required to meet business objectives.
-
Variety evaluates the types of data involved (structured, unstructured, or semi-structured) and their relevance to the defined business problem.
-
Veracity measures data quality, reliability, bias, and uncertainty, which directly impact trust, fairness, and risk in AI outcomes.
-
Value ensures that the data, if used, can realistically contribute to measurable business benefits and decision improvement.
From a CPMAI perspective, these properties are not technical characteristics but decision criteria used to validate data feasibility, identify constraints, and support a Go / No-Go recommendation. If data volume is insufficient, velocity cannot be supported, variety is irrelevant, veracity is compromised, or value cannot be demonstrated, the AI initiative must be paused, redesigned, or stopped before moving to Phase III.
CPMAI Phase II – Scenario MCQs (Data Understanding)
Q1.
A retail organization wants to use AI to predict customer churn. During Phase II, the team realizes that "churn" is defined differently by sales and marketing teams. What should be done first?
A. Start data collection using both definitions
B. Select the definition with more data
C. Standardize the business definition of churn
D. Proceed and resolve later during modeling
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Phase II requires clear target variable definition before any data analysis begins.
Q2.
An AI project requires customer interaction data, but access is restricted due to departmental ownership. What Phase II issue does this represent?
A. Data quality problem
B. Data availability and accessibility constraint
C. Data labeling issue
D. Model feasibility issue
✅ Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Phase II explicitly assesses data ownership, access, and silos.
Q3.
Which data type is MOST suitable for sentiment analysis in a customer feedback AI project?
A. Structured transactional data
B. Numerical time-series data
C. Unstructured textual data
D. Reference master data
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Sentiment analysis relies primarily on unstructured text data.
Q4.
A dataset has high volume but contains outdated records that no longer reflect current business conditions. Which data quality dimension is MOST affected?
A. Accuracy
B. Completeness
C. Timeliness
D. Consistency
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Timeliness ensures data reflects current and relevant conditions.
Q5.
An AI team discovers that historical loan approval data reflects past discriminatory practices. What Phase II concern does this raise?
A. Model overfitting
B. Algorithm selection
C. Data bias and fairness risk
D. Infrastructure limitation
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Phase II requires bias identification before data is used for modeling.
Q6.
Which activity BEST represents translating a business problem into data requirements?
A. Choosing a machine learning algorithm
B. Defining input features and target variables
C. Selecting cloud infrastructure
D. Training a pilot model
✅ Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Phase II focuses on mapping business objectives to data elements.
Q7.
A project team plans to use social media data for AI analysis. What Phase II check is MOST critical before proceeding?
A. Feature engineering complexity
B. Data storage cost
C. Legal and consent compliance
D. Model explainability
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: External data sources require privacy, consent, and legal validation.
Q8.
Which outcome indicates that Phase II should recommend a No-Go decision?
A. Data exists but requires cleaning
B. Data quality is low but improvable
C. Data cannot be legally or ethically used
D. Data labeling will take time
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: If data cannot be used legally or ethically, CPMAI requires stopping or redesigning the initiative.
Q9.
A team assumes more data will automatically improve AI outcomes. Which CPMAI principle does this violate?
A. Model interpretability
B. Data sufficiency over quality
C. Algorithm efficiency
D. Automation maturity
✅ Correct Answer: B
Explanation: CPMAI prioritizes data relevance and quality over volume.
Q10.
Which document is a key deliverable of Phase II?
A. Model performance report
B. Data requirements and inventory document
C. Deployment architecture
D. Monitoring dashboard
✅ Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Phase II deliverables focus on data understanding, sources, and readiness.
Q11.
A dataset has inconsistent formats for the same attribute across systems. Which data quality issue is this?
A. Accuracy
B. Completeness
C. Consistency
D. Bias
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Consistency ensures the same meaning and format across datasets.
Q12.
Which Phase II decision MOST directly impacts future model explainability?
A. Choice of algorithm
B. Feature selection and data definition
C. Compute infrastructure
D. Model deployment method
✅ Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Explainability begins with transparent, well-defined data and features.
Q13.
An organization decides to enrich internal data with third-party market data. This activity belongs to which Phase II outcome?
A. Algorithm optimization
B. Data gap remediation
C. Model tuning
D. Performance validation
✅ Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Phase II identifies data gaps and enrichment strategies.
Q14.
Which statement BEST reflects CPMAI guidance for Phase II?
A. Model accuracy determines AI success
B. Data preparation is a Phase IV activity
C. Data feasibility must be validated before modeling
D. Algorithms can compensate for poor data
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Phase II exists specifically to validate data feasibility early.
Q15.
Who is MOST responsible for validating data relevance during Phase II?
A. AI engineer
B. Data scientist
C. Business stakeholder
D. Infrastructure architect
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: CPMAI stresses business ownership of data relevance, not technical teams alone.
Q16.
An AI initiative requires real-time decision-making, but available data is updated only once per day. Which Big Data property represents the primary constraint?
A. Volume
B. Variety
C. Velocity
D. Veracity
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Velocity evaluates whether data is generated and processed at the speed required to meet business objectives.
Q17.
A project team has access to large amounts of customer data, but much of it is irrelevant to the defined business problem. Which Big Data property is most impacted?
A. Volume
B. Variety
C. Value
D. Velocity
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Value assesses whether data can realistically contribute to measurable business outcomes, not just whether it exists.
Q18.
An AI model is trained using data from only one geographic region, leading to unfair outcomes when applied globally. Which Big Data property should have been evaluated more carefully in Phase II?
A. Volume
B. Veracity
C. Velocity
D. Value
✅ Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Veracity includes data bias and representativeness, which directly affect fairness and trustworthiness of AI outcomes.
Q19.
An organization has high-quality, relevant data, but the dataset is too small to support statistically reliable predictions. Which Big Data property is the primary concern?
A. Variety
B. Velocity
C. Volume
D. Veracity
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Volume determines whether sufficient data exists to support meaningful AI analysis and prediction.
Q20.
An AI initiative requires analyzing customer emails, call recordings, and transaction logs together. Which Big Data property is MOST relevant during Phase II assessment?
A. Volume
B. Velocity
C. Variety
D. Value
✅ Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Variety evaluates the presence and relevance of multiple data types (structured and unstructured) required for the AI use case.
